人工智能数学之范数
范数
概念
范数是一种强化了的距离概念,包含向量范数和矩阵范数。线性代数中我们知道一个向量(m1)通过一种映射关系(矩阵 nm),可以得到另一组向量(n*1)。其中向量范数表示了向量空间中,这个向量的大小,因为向量都是有大小的,所以度量就使用了范数 。矩阵范数,表示在这个映射中,变化大小的度量。
向量范数
L-P范数
L-P范数作为一组范数,定义如下:
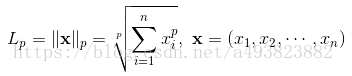
L0范数
P=0的范数,当p=0,数学层面上很不容易解释,所以通俗上讲L0范数就是表示向量中非零元素的个数。
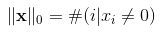
L1范数
P=1的范数,当P=1时,X向量的每个元素的p次方求和后开1/p次方,带入1之后得:
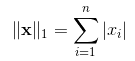
通俗上讲L1范数就是表示向量中非零元素绝对值之和。L1范数扩展开有很多形式,例如曼哈度距离、最小绝对误差,例如两个向量之间差异,SAD(Sum of Absolute Difference)绝对误差:
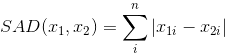
优化L1范数:
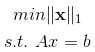
L1可以实现特征的稀疏,去掉没用的信息。
L2范数
L2范数是我们平常使用很多的,例如距离度量的欧氏距离就是L2范数。P=2,带入L-P公式
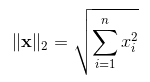
通俗上讲就是向量元素平方求和后开平方。
和L1范数一样,L2范数也可以度量两个向量之间的差异,平方差和(Sum of Squared Difference)
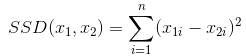
优化L2范数:
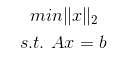
L2也常用在做机器学习模型中优化目标函数时的正则化项,防止过拟合。
L-∞范数
当P值为∞时,L无穷范数主要是度量向量元素的最大值。
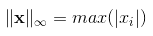
矩阵范数
1-范数(列和范数)
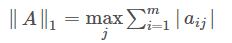
将矩阵的列方向进行绝对值求和,选择数值最大的作为矩阵的1-范数。
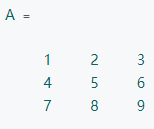
A的1-范数就是第三列的值,18.
∞-范数(行和范数)
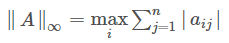
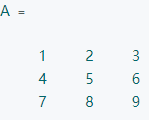
A的∞-范数就是第三列的值,24.
2-范数(A*A最大特征值开方)
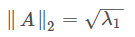
共轭转置矩阵
A* 指的是A的共轭转置矩阵,如果A矩阵内全部都是实数,A的共轭转置矩阵就和A转置一样,如果A矩阵内有复数,就先对A去共轭(各项的实数不变,虚数取相反数)然后在进行转置。
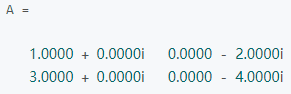
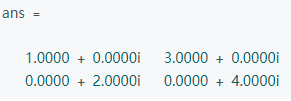
特征值
矩阵A的特征值定义为:
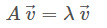


V中每一列都是一个特征向量,D中对应的值就是特征向量的特征值。第一列为例,特征值为16.1168,对应v中第一列特征向量。

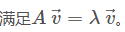
2-范数
矩阵的2-范数即对矩阵A*A最大特征值λ1开方。

则矩阵的2-范数是16.8481。
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/Michael__Corleone/article/details/75213123
https://blog.csdn.net/yangpan011/article/details/79461846
https://blog.csdn.net/u013534498/article/details/52674008
https://blog.csdn.net/shijing_0214/article/details/51757564
本文地址:http://www.45fan.com/a/question/99621.html
